2025
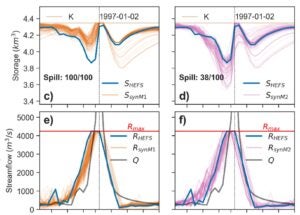
Develops a validation framework for synthetic ensemble hydrologic forecasts based on reservoir operations under forecast-informed policies.[Github]
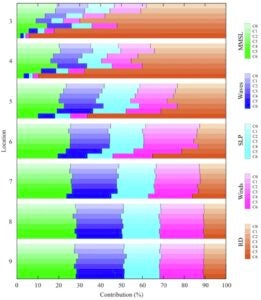
Investigates the impacts of climate change induced sea-level rise and higher river discharge on the magnitude and frequency of flooding events as well as the relative importance of various forcing drivers to compound flooding.

Develops an optimal control technique to maximize vertical pullout capacity of flexible embedded structures of arbitrary nonlinear shape.
2024

Combines a top-down and bottom-up approach to climate vulnerability assessment using exploratory scenarios developed through thermodynamic and dynamical-guided perturbations. [Github].

A hybrid statistical-dynamical framework for compound coastal flooding analysis that integrates a stochastic generator of compound flooding drivers, a hydrodynamic model, and a machine learning-based surrogate model, demonstrated for San Francisco (SF) Bay.
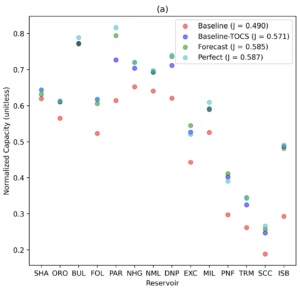
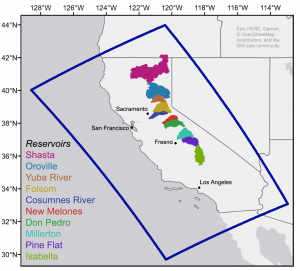
Investigates the potential forecast-informed reservoir operations (FIRO) to increase water supply while minimizing additional flood risk at 14 reservoirs in the Sacramento, San Joaquin, and Tulare river basins. [Github].
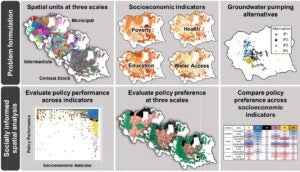
Impact of spatial scale on multi-objective planning for urban groundwater modeling to determine relationship between policy preference and socioeconomic indicators. [Github].
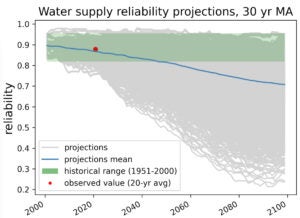
Detect changes in water supply and flood performance outside the envelope of natural variability, and attribute the timing of these detections to uncertain drivers. Train a logistic regression classifier to predict future detections given recent observations. [Github].
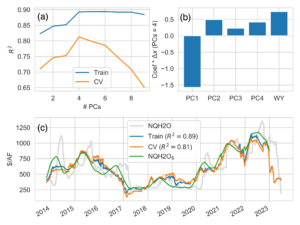
Principal component regression to predict the forward six-month average of the NQH2O index based on reservoir storage anomalies and ensemble inflow forecasts. A threshold-based hedging strategy uses the forecast model to reduce the risk of price increases following allocation announcements from SWP/CVP.
2023
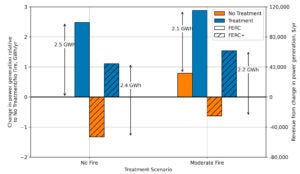
Models the impact of forest restoration on wildfire behavior, hydropower generation, and environmental flows in the Middle Fork American River Basin, California. [Github]
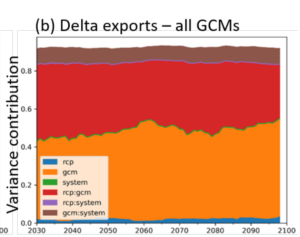
Method to investigate whether the total uncertainty in output metrics is primarily attributable to the climate ensemble or to the systems model itself, combining time series error models with time-varying Sobol sensitivity analysis. [Github]
2022
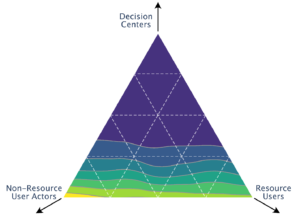
Generalized modeling framework to understand the structural features impacting the stability of resource governance systems, including the heterogeneity and connectivity of actors. [Github]
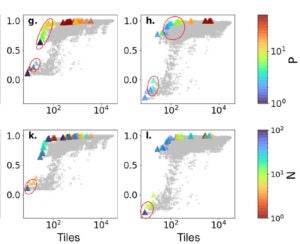
Determines optimal tile configuration for a target level of spatially distributed model complexity as a multi-objective problem.
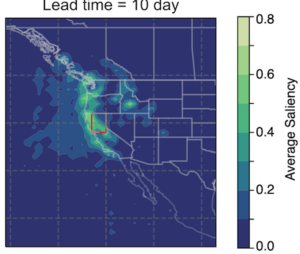
Deep learning models trained on images of GEFS precipitation forecasts to classify the occurrence of heavy precipitation for a target region. Analyzes network activation across lead times. [Github]
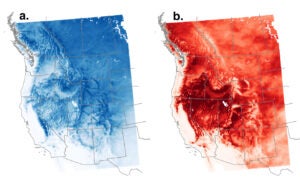
Investigates projected patterns in changing precipitation phase for mountain areas of the western United States over the 21st century and how shifts from snow to rain may impact runoff and reservoir storage.
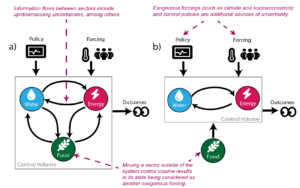
Reviews challenges to the goal of characterizing, attributing, and quantifying uncertainty in multi-sector systems, including inference and model calibration, simulation, and sensitivity analysis.
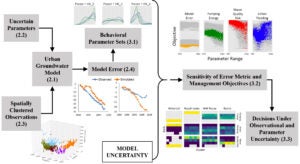
Determines the importance of observation choice and parameter values on aquifer management objectives when controlling for model error, and compares how the relative performance of management alternatives varies when exposed to endogenous uncertainties. [Github]
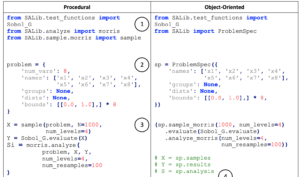
Describes recent and planned updates to the SALib package for global sensitivity analysis, focused on simplifying applications, interpreting results, and fostering a community of practice.
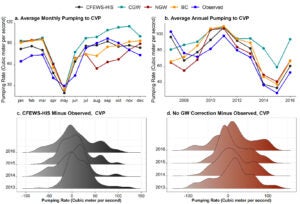
Investigates how model projection errors influence assessments of water availability and financial stability for irrigation districts in California.
2021
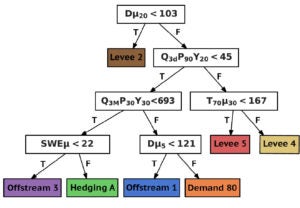
Framework for dynamic adaptation of water resources systems under climate and land use uncertainty by designing and testing policies that combine relevant indicators, actions, and thresholds in a flexible structure. [Github].
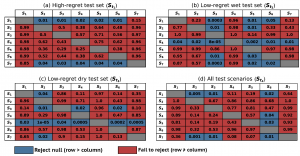
Investigates the relationship between scenario properties (annual runoff, snowpack, and baseline regret) and the ability of policies to generalize out of sample. [Github].
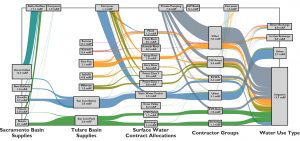
CALFEWS simulation model connecting statewide inter-basin transfers with conjunctive water management strategies at the scale of irrigation and water storage districts. [Github].
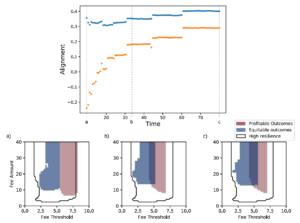
Dynamical systems model of asymmetric resource access in resource-based communities linking industrial resource degradation, community well-being, and migration in response to economic and resource conditions. [Github].
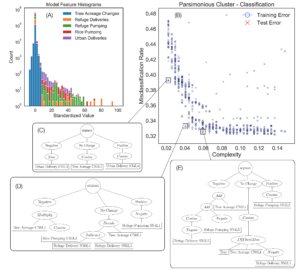
Automated generation of model structure to describe human behavior in water systems using symbolic regression. Evaluation along performance-complexity tradeoff, and sensitivity analysis of resulting model structures. [Github].
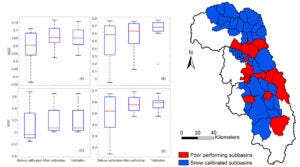
Multivariate calibration of SWAT models for the Tulare Basin, California to evaluate changes in runoff timing due to current and future snowpack decline.
2020
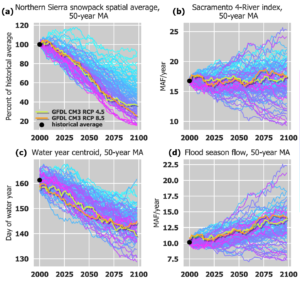
Adaptations by parameterizing the structure of existing policies using a dynamic flood control rule curve and revised snowpack-to-streamflow forecasting methods. [Github].
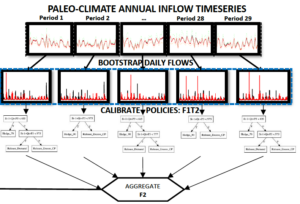
Extensions of bagging and cross-validation techniques for policy search problems using streamflow resamples from the paleo record.
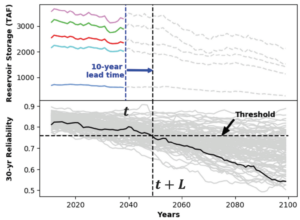
Dynamic classification of the occurrence of water supply vulnerability to climate change, represented by the long-term moving average of reliability falling below a threshold. [Github].
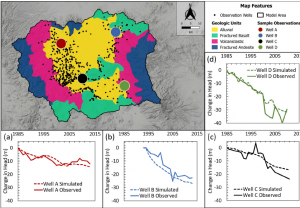
Comparing managed recharge alternatives to reduce the effect of historical overdraft using a physically-based groundwater model.
Review article framing dynamic adaptation to climate change as an optimal control problem. Discussion of challenges that arise due to multiple sources of uncertainty.
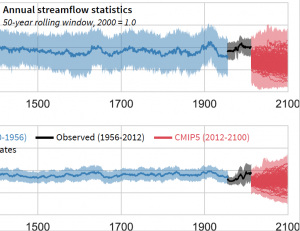
Modifying process representation in the coupled WRF/Noah-MP model to improve hydrologic simulation upstream of California reservoirs.
Optimization-based design of satellite constellations for near-continuous global coverage.
2019
Sensitivity analysis of a global groundwater model using Method of Morris.
Analysis of perennial crop data and implications for water supply derived from pesticide permits over the period 1974-2016. [Github].
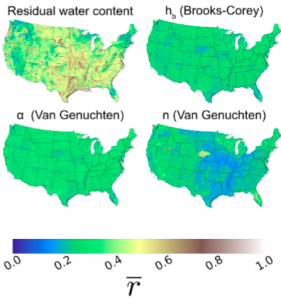
High-resolution soil dataset with reduced uncertainty compared to standard prior distributions used in land surface model calibration.
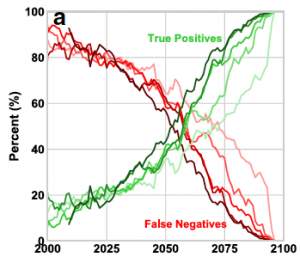
A statistical testing approach for threshold-based classifiers of vulnerable scenarios in long-term streamflow projections. [Github].
2018
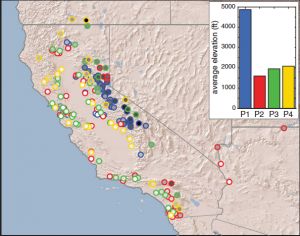
Clustering California reservoirs based on typical behavioral profiles.
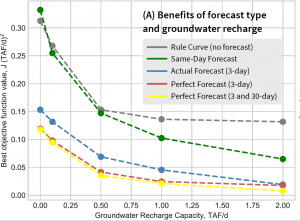
Extension of policy tree optimization method using synthetic ensembles of streamflow forecasts for reservoir control, including groundwater banking.
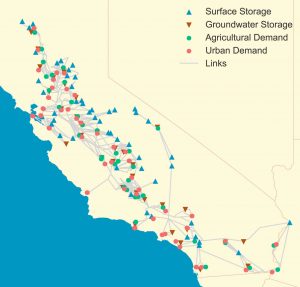
Short communication describing open-source version of the CALVIN model with LP solver performance benchmarks. [Github].
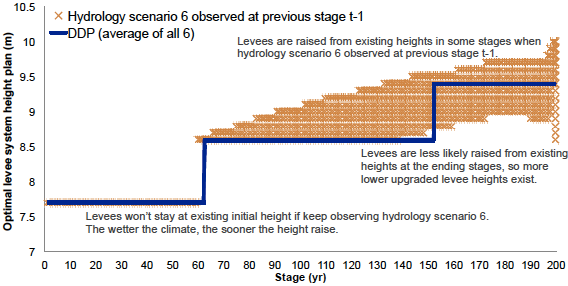
Adaptive levee planning with nonstationary flood risk, using stochastic dynamic programming.
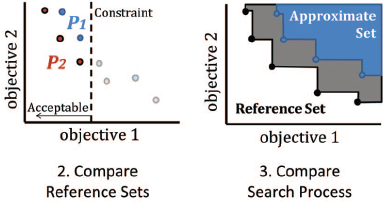
Impact of preference constraints (i.e., optional constraints on objective values) on the performance of multi-objective evolutionary algorithms.
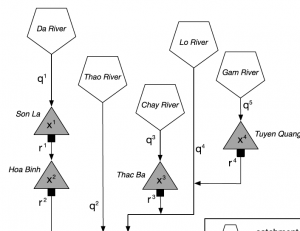
Policy search for multi-reservoir systems using a hierarchical parallelization scheme, using both deterministic and stochastic hydrology.
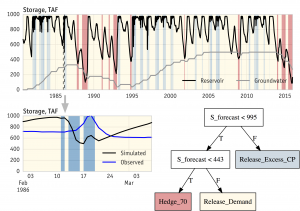
Binary tree policy search for control of dynamic systems. Uses a heuristic simulation-optimization approach. [Github].
2017
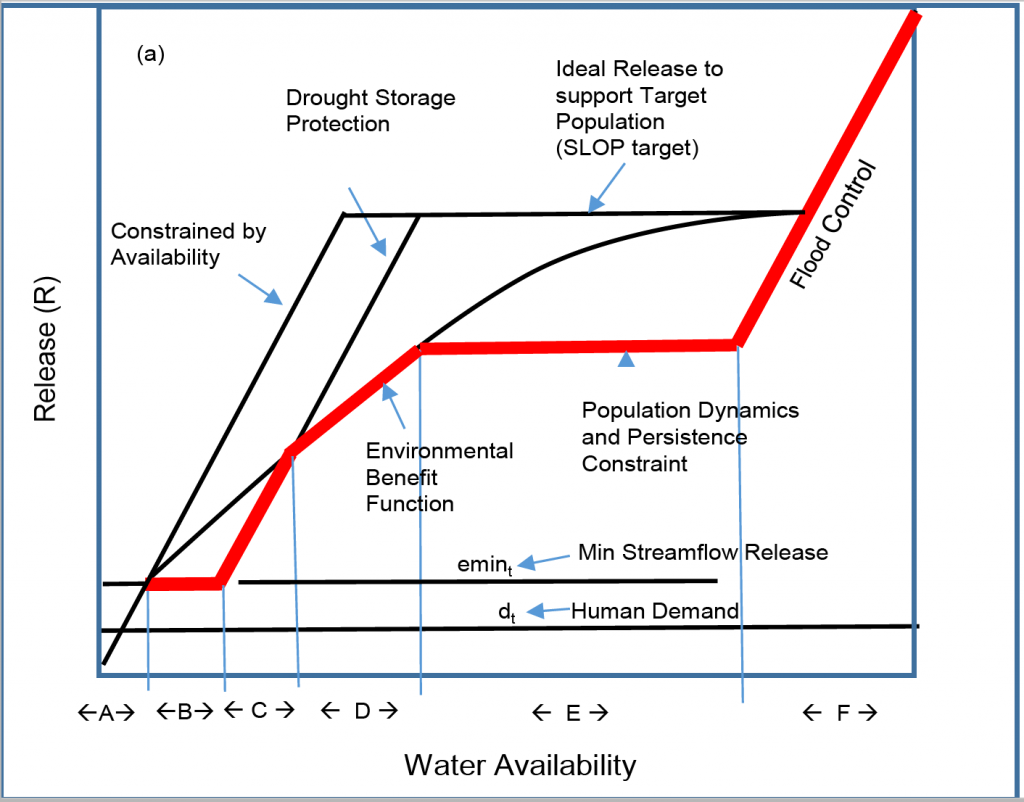
An approach for reservoir operation to incorporate downstream biological objectives without sacrificing water supply reliability. The method is applied for fall-run Chinook salmon in the Lower American River.
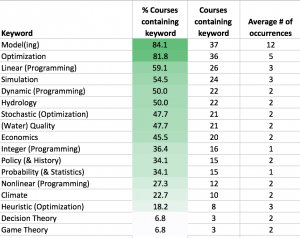
An editorial based on the results of practitioner interviews and analyzing course syllabi from the systems analysis field.
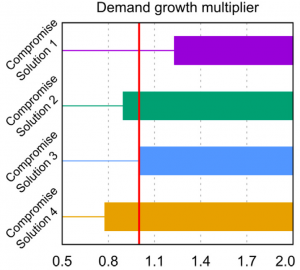
Optimization of decision alternatives across an ensemble of deeply uncertain scenarios, rather than optimizing to historical observations and then simulating the ensemble.
Implementations of the Sobol, Morris, FAST, and Delta methods, among others. [Github]
2016
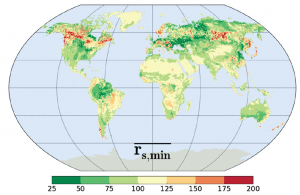
Estimating the mean and variance of global parameter values using extra-trees regression, after first reducing the dimension of the parameter space using sensitivity analysis.
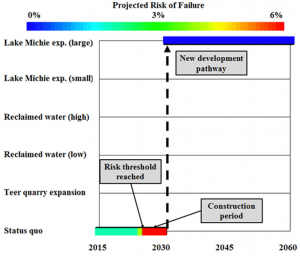
Multi-objective optimization for urban water utilities combining long-term infrastructure development with short-term conservation options, where decisions are triggered by thresholds of a risk metric.
Modifies a synthetic streamflow generation technique to allow user-defined frequency and severity of droughts while preserving autocorrelation and spatial correlation. [Github].
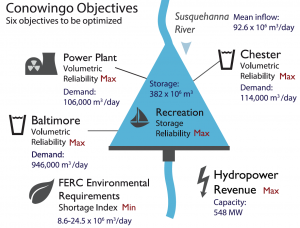
A comparison of multi-objective optimization methods for a single-reservoir direct policy search problem. Uses MOEAFramework and Borg MOEA.
2015
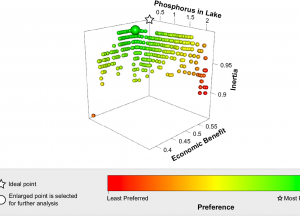
The OpenMORDM library for decision making under deep uncertainty. [Github]
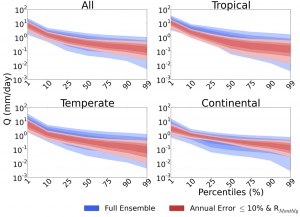
Large-scale ensemble evaluation of VIC model parameters on a global grid. Constraining ensemble members with observed data and calculating parameter sensitivity using the CDF distance metric.
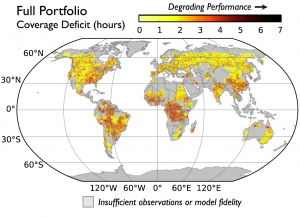
Analyzing and optimizing coverage of satellite constellations for rainfall observation.
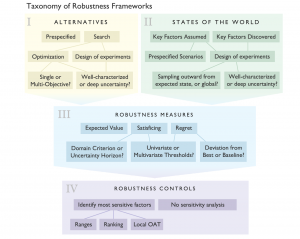
A review of frameworks for decision making under deep uncertainty, where the probabilities of future scenarios are difficult to quantify.
Earlier
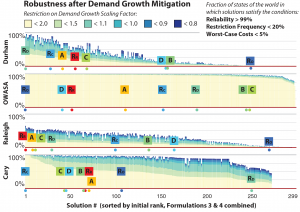
Given a set of multi-objective solutions optimized under historical conditions, this study subjects them to a range of hydrologic and economic uncertainties to identify the most robust solutions.
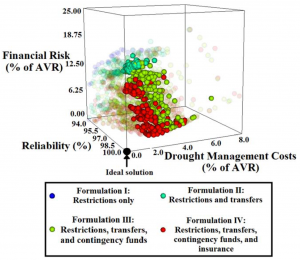
Multi-objective portfolios of water conservation and transfer options for urban water utilities to maintain supply reliability and reduce financial impacts of drought.
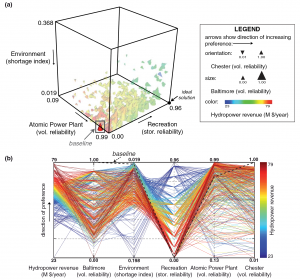
Identifying an existing reservoir operating policy from historical data using a network of radial basis functions, and re-optimizing the policies for multiple objectives across an ensemble of synthetic streamflows.
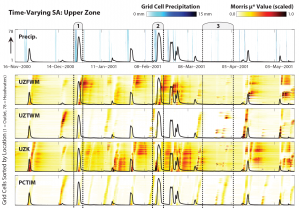
Parameter sensitivity computed at a three-hour timestep and compared to aggregate event-scale sensitivity to improve process understanding of a spatially distributed hydrologic model.
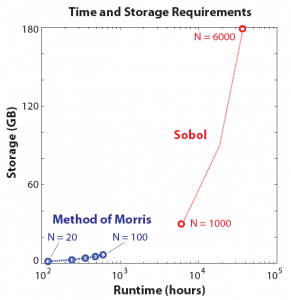
For a spatially distributed watershed model, we show that the Morris method can produce parameter sensitivity values and rankings similar to the Sobol method, with significantly reduced computation time.
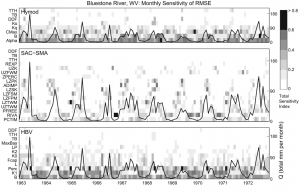
Sobol sensitivity analysis of three hydrologic models (Hymod, HBV, SAC-SMA) at monthly and annual timesteps, performed across a hydroclimatic gradient of 12 watersheds in the US.
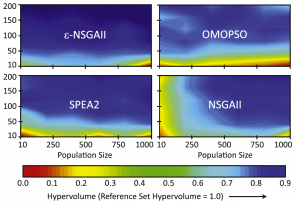
A comprehensive diagnostic comparison of state-of-the-art optimization methods for multi-objective problems, using three real-world case studies: hydrologic model calibration, water supply planning, and groundwater monitoring. Uses MOEAFramework and Borg MOEA.